MIG wire selection affects weld quality, spatter levels, and penetration depth. Choosing the right wire depends on base metal composition, surface condition, and shielding gas—not just diameter and tensile strength.
Common MIG Wire Classifications
ER70S-6 (Most Common)
- Deoxidizers: Manganese, silicon
- Tensile strength: 70,000 PSI minimum
- Best for: Dirty or rusty steel, single-pass welds, general fabrication
- Shielding gas: 75/25 Ar/CO₂ or 100% CO₂
- Spatter level: Moderate
ER70S-3
- Deoxidizers: Lower manganese and silicon than ER70S-6
- Tensile strength: 70,000 PSI minimum
- Best for: Clean steel, multi-pass welds, automotive sheet metal
- Shielding gas: 75/25 Ar/CO₂ (100% CO₂ not recommended)
- Spatter level: Low
ER308L (Stainless Steel)
- Composition: 19-21% chromium, 9-11% nickel
- Best for: 304/304L stainless steel
- Shielding gas: 90/10 Ar/CO₂ or tri-mix (He/Ar/CO₂)
- Corrosion resistance: Excellent
ER316L (Stainless Steel)
- Composition: 18-20% chromium, 11-14% nickel, 2-3% molybdenum
- Best for: 316/316L stainless, marine environments, chemical processing
- Shielding gas: 90/10 Ar/CO₂ or tri-mix
- Corrosion resistance: Superior (molybdenum addition)
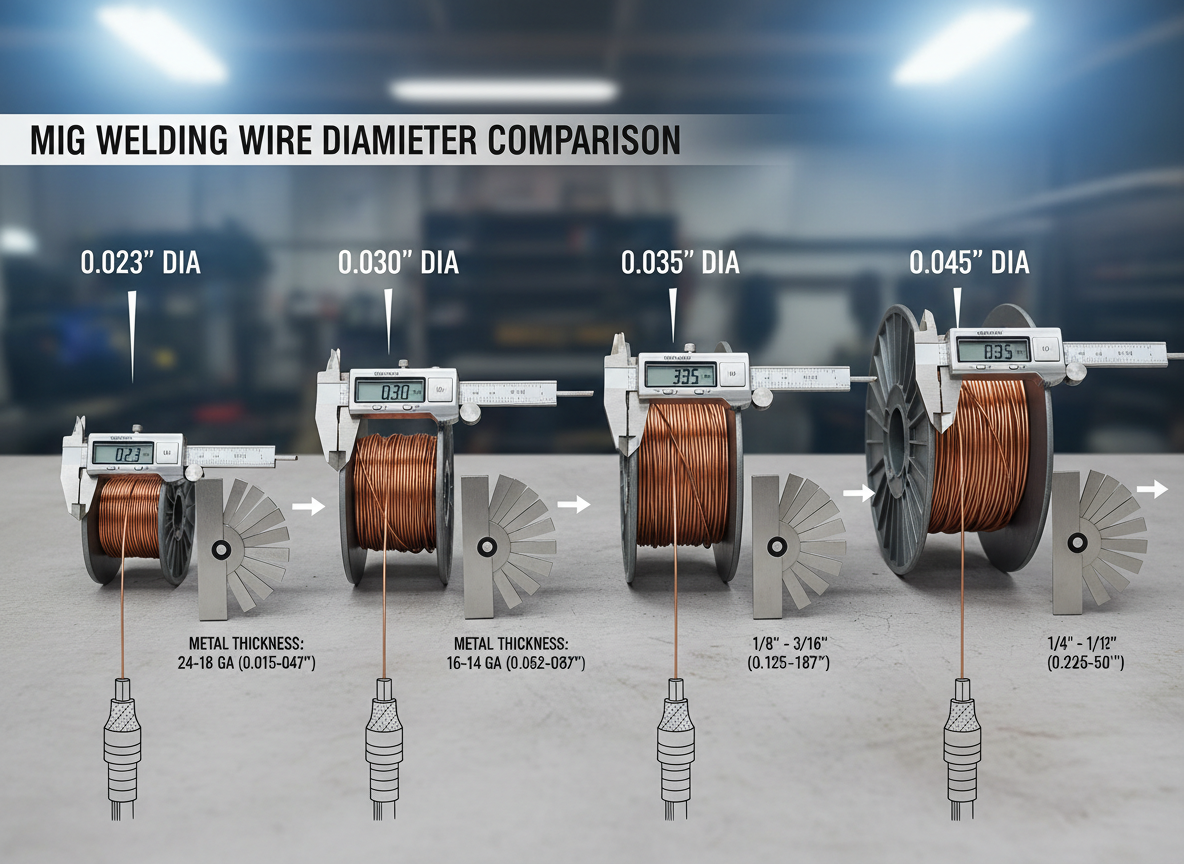
Wire Diameter Selection
| Diameter | Amperage Range | Material Thickness | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.023” | 30-130A | 24-18 gauge | Automotive sheet metal, thin tubing |
| 0.030” | 40-145A | 18-14 gauge | General fabrication, light structural |
| 0.035” | 50-180A | 14 gauge-1/4” | Most common all-purpose size |
| 0.045” | 75-250A | 1/4”-1/2” | Heavy structural, thick plate |
| 0.052” | 100-300A | 1/2”+ | Industrial fabrication, heavy equipment |
Rule of thumb: Thinner wire = better control on thin material. Thicker wire = faster deposition on heavy plate.
Shielding Gas Impact on Wire Performance
75/25 Argon/CO₂ (C25)
- Pros: Low spatter, smooth arc, good bead appearance
- Cons: Higher cost than 100% CO₂
- Best for: ER70S-3, ER70S-6, stainless steel
100% CO₂
- Pros: Deep penetration, low cost
- Cons: Higher spatter, rougher arc
- Best for: ER70S-6 on thick steel (not recommended for ER70S-3)
90/10 Argon/CO₂
- Pros: Minimal spatter, excellent for stainless
- Cons: Shallow penetration on carbon steel
- Best for: ER308L, ER316L stainless wire
Surface Condition Requirements
| Wire Type | Mill Scale | Light Rust | Heavy Rust | Clean Steel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER70S-6 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| ER70S-3 | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| ER308L | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| ER316L | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
ER70S-6 advantage: Higher deoxidizers clean impurities during welding. ER70S-3 requires clean base metal to avoid porosity.
AWS Filler Metal Specifications
AWS A5.18 (Carbon Steel MIG Wire) – Covers ER70S-3, ER70S-6, and other carbon steel wires – Defines chemical composition, tensile strength, and elongation requirements
AWS A5.9 (Stainless Steel MIG Wire) – Covers ER308L, ER316L, and other stainless wires – Specifies corrosion resistance and ferrite content
Wire Storage & Handling
Moisture Contamination – Causes: Porosity, hydrogen cracking – Prevention: Store in sealed containers with desiccant packs – Shelf life: 12 months (carbon steel), 6 months (stainless)
Wire Feed Issues – Kinked wire = erratic arc and bird-nesting – Solution: Use proper spool tension and liner size
Liner Compatibility
| Wire Diameter | Liner Inside Diameter |
|---|---|
| 0.023”-0.030” | 0.030”-0.035” |
| 0.035” | 0.035”-0.045” |
| 0.045” | 0.045”-0.052” |
| 0.052” | 0.052”-0.062” |
Oversized liner = wire wander. Undersized liner = excessive friction and burnback.
Common Mistakes
Using ER70S-3 on rusty steel
Low deoxidizers can’t compensate for surface contamination. Result: porosity and weak welds. Use ER70S-6 or clean the base metal.
Wrong liner size for wire diameter
0.035” wire in 0.045” liner causes erratic feeding. Match liner to wire diameter within 0.005”-0.010”.
Storing stainless wire without moisture protection
Stainless wire absorbs moisture faster than carbon steel. Always use sealed containers with desiccant.
Buying Checklist
- ✓ Wire classification matches base metal (ER70S-6 for dirty steel, ER70S-3 for clean)
- ✓ Diameter suits material thickness and amperage range
- ✓ Shielding gas compatible with wire type
- ✓ AWS A5.18 or A5.9 certification marked on spool
- ✓ Liner size matches wire diameter
- ✓ Storage container includes moisture protection
- ✓ Spool size fits your machine (2 lb, 10 lb, 33 lb, 44 lb)







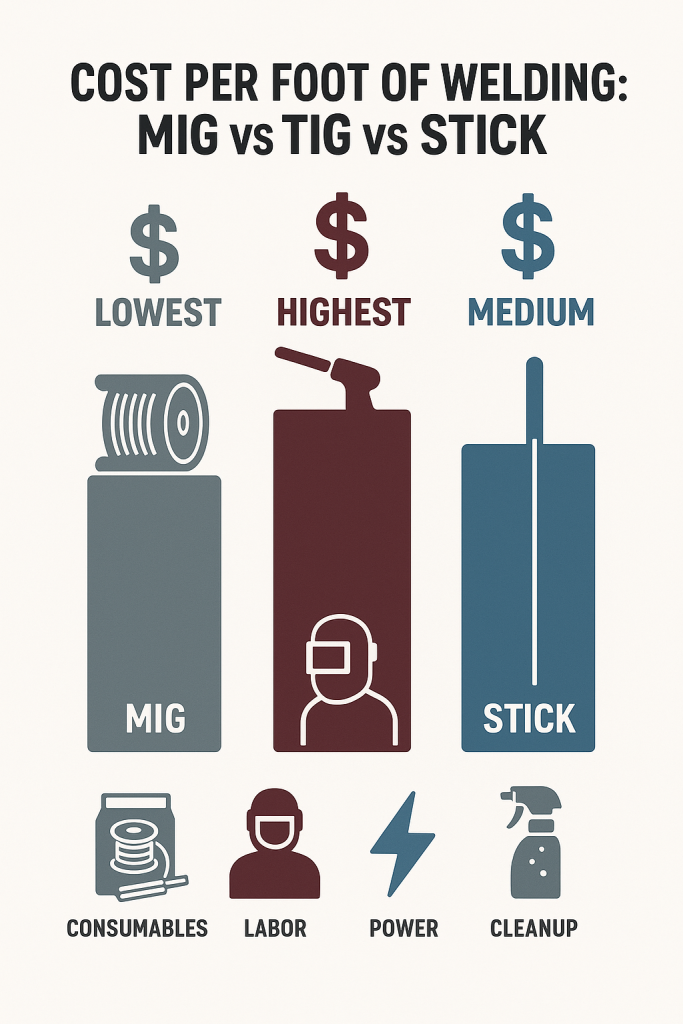
 MIG Welding (GMAW) – High Speed, Low Cost
MIG Welding (GMAW) – High Speed, Low Cost
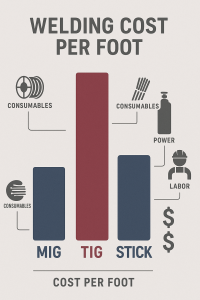
 Assumptions:
Assumptions: MIG Welding Cost Example
MIG Welding Cost Example $0.89/ft
$0.89/ft